Clipboard
Cut
Copy
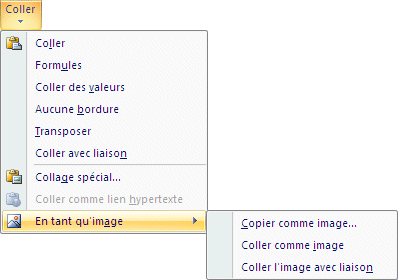
Paste
PasteThis option works like the basic Paste command. It will either copy the text, the value or the formula from the source cell into the selected cells. Formulas
Paste values
No border
Transpose
OR
The same data series are now in vertical instead of horizontal. Paste link
OR
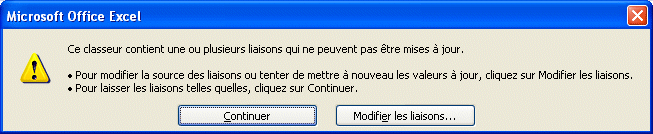
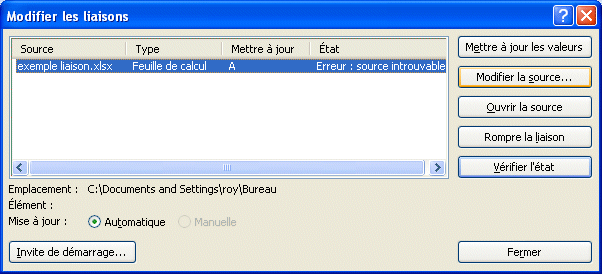
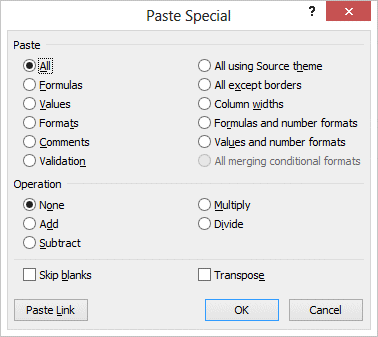
Paste specialThe previous options couvered the elements that are most often used. But they don't cover all the possible options.
Clipboard options
Move clipboard
To move the clipboard:
To change the size of the clipboardclipboard:
To close the clipboard:
Fonts
Fonts
|
This option determines the size of the font. You can change the size of the text at any time to better correspond with your needs. |
Increase/Decrease Font Size
Another way to change the size the text is to use the buttons increase or decrease the font size. The changement is immediate. |
Bold
![]() The Bold command allows you to put more emphasis on your text whether
its for a title or the result of a mathematical formula.
The Bold command allows you to put more emphasis on your text whether
its for a title or the result of a mathematical formula.
Italic
![]() The italic command also allows you to put some emphasis on a part
of your text.
The italic command also allows you to put some emphasis on a part
of your text.
Underline
 The underline and double underline is another way
of place the emphasis on text to determine its importance.
The underline and double underline is another way
of place the emphasis on text to determine its importance.
Borders
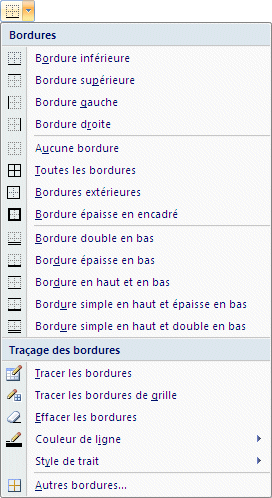 |
You can also place a border around a cell, or a range of cells, to improve your workbook's presentation. The options under the Border command will offer many options to determine the location, the border's thickness, the color and type of line for your borders. At the end of the list, the More Borders option will give you even more control on all the possible options. |
Fill color
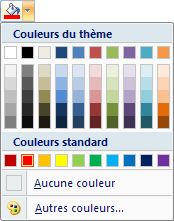 |
This option allows you to determine the cell's fill color. From this window,you have access to 66 different colors. The More Colors option allows you to choose among more than 16 million colors. |
Other colors
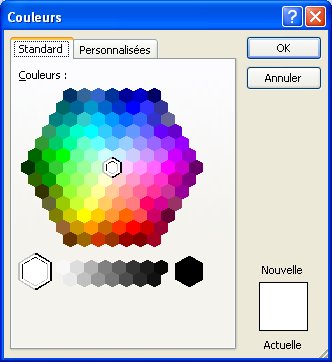
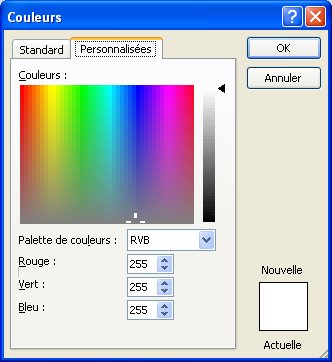
The standard tab offers a colors pallet with the most popular colors. The personalize tab gives you a precise control on the colors that you want. You can give one value of 0 to 255 to each basic color: red, green and blue. The total is 16 777 216 possible colors. |
Font color
 |
This option determines the color of the text that you written. You have access to the same options than the Fill colors described above. |
Font Options
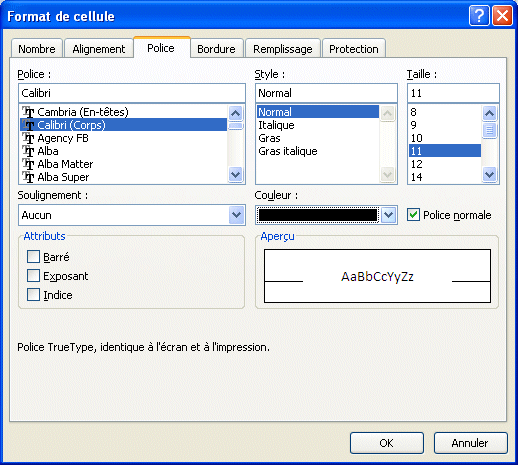 |
From this tab, you can select the font type, its style and size, the type of underline, font color and some other attributes. You also have a preview box that will show you the results of your choices. Once you're comfortable with your font choices, you can press the OK button. Otherwise, you can always press the Cancel button. |
Alignment
 |
The alignment determines where the content of the cell will appear inside it. Will it be placed to the left, the center or the right side of the cell? You can add an indentation, a space between the cell border and the text, or change the text's orientation; put the text at an angle. |
Horizontal
![]() Places the content of the cell to the left, right or center of the cell.
Places the content of the cell to the left, right or center of the cell.
Vertical
![]() Place the content of the cell on top, centre or bottom of the cell. This has an impact if the cell's height is greater than normal.
Place the content of the cell on top, centre or bottom of the cell. This has an impact if the cell's height is greater than normal.
Orientation
 |
Excel doesn't limit to write your text horizontally. You can change the text's orientation to place some emphasis on the text or on a title.
Other orientation options are available under the Dialog box launcher button at the bottom right of this group of commands. |
Decrease/Increase Indent
This determines the amount of space between the content and the cell's border. You can add more or less space between the text and the left cell border. |
Wrap text
|
When the content of the cell is longer than the length of the cell, the text continues in the cell to the right if that cell is empty. Otherwise you will only see the leftmost section of the text. However, you can write as many rows of text in the same cell. The Wrap text option changes automatically the height of the cell so that you can see all the text that was entered. You can also use the combination of ALT and Enter keys to indicate where you want start writing on the next line. |
Merge and center
 |
An interesting option is to "merge" many cells together either in rows or columns into a single cell. It's very practical when you write a title that extends over many rows or columns. |
![]() Select the range of cells from that you want regroup by one only.
Select the range of cells from that you want regroup by one only.
![]() Press the Merge and center.
Press the Merge and center.
Options for Alignment
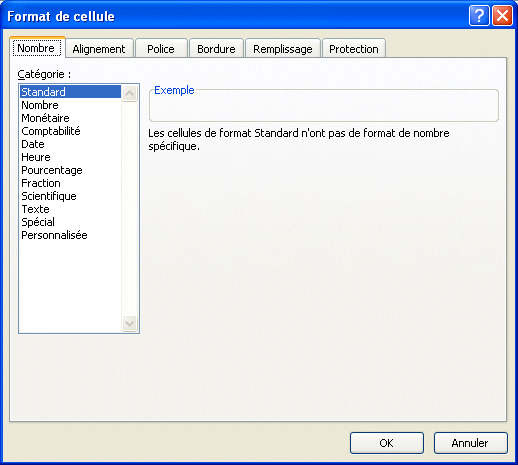 |
You must view the options to master all the possible options. Those that have already used Excel 2003 or a previous version will be on familiar grounds. Except for a few changes to the presentation, you will find the same six tabs that where in previous versions of Excel. Experiment with these options and bring out a better presentation for your model. |
Number
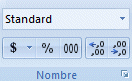 |
Microsoft Excel offers many formatting styles for text, values and even for dates and times.
|
Number
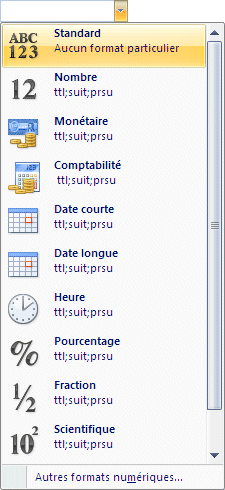 |
By pressing the arrow at the end of the box, you have a short list of available formats for values, text, dates and times. The last option, Other formats, allows you to choose among a greater formatting list and even to personalize to your own presentation style. |
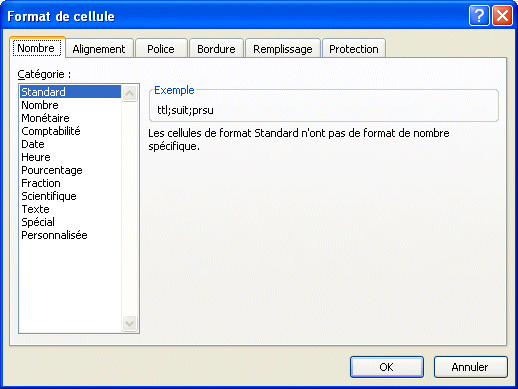 |
By selecting Other formats from the last menu, or by pressing the dialog box launcher box from Number group of commands, you will access all the possible formatting styles and options. The Personalize category allows you to add your own formats. There are also the other tabs, identical from the Excel 2003 and previous versions that allows you to change the cell's formatting in many ways. |
Currency
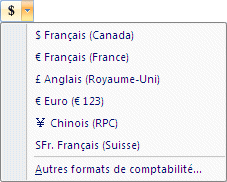 |
There are many possibilities under the Currency number format. Is it in dollars, in Euros, Yens or another denomination?
|
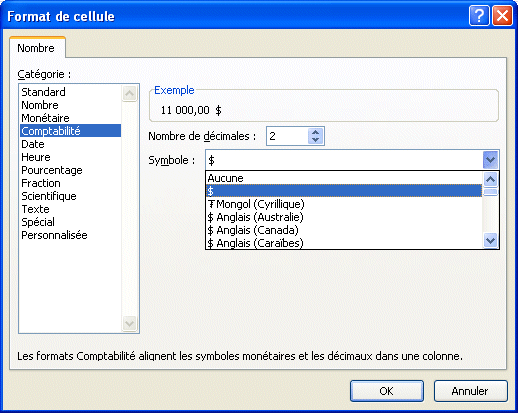 |
From the Accounting category, you can choose among many more denominations than the ones mentioned in the previous list. |
Percent
![]() Place the value in percent style. The value 0,25 becomes 25%, 15 becomes 1500%.
Place the value in percent style. The value 0,25 becomes 25%, 15 becomes 1500%.
Comma
![]() Splits the value by groups of thousands. Ex. 2500 becomes 2 500, 1300000 becomes 1 300 000.
Splits the value by groups of thousands. Ex. 2500 becomes 2 500, 1300000 becomes 1 300 000.
Increase/Decrease decimals
Allows to add or to remove decimal values from the formatting. Excel will round up the value according to the number of decimals that you want show. |
Styles
 |
You can also apply formatting styles to cells, a range of cells or to tables. The next section will give more information on how to use these options. |
Conditional formatting
Conditional formatting is one of the most under used options in Excel. The cell's formatting will change when a condition occurs. For example, the cell could turn red when the value is under a predetermined level. You may need to keep a minimal quantity of parts in inventory. Or a ratio is too high and you want to be warned when that happens.
Microsoft added a lots of conditional formatting options with Excel 2007. It would be to your advantage to look over these options with the exercice that was prepared for you.
![]() Follow this link to view the exercise for this command
Follow this link to view the exercise for this command
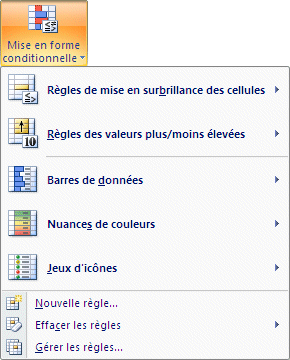 |
Conditional formatting gives you the option to change a cell's formatting (border, fill color, font color) when a condition is reached. For example, you could ask Excel to turn the cell red when a value turns negative or when the inventory for product reaches a critical level. You can apply many conditionnal formatting the same cell. The conditional formatting options are elements of Excel that has been greatly improved with Excel 2007. Not, only does it allows you to change the formatting of a cell according to its value, but it allows you to realize some analysis on a range of values. This was only possible with specialized software before the arrival of Excel 2007. |
Highlight Cells rules
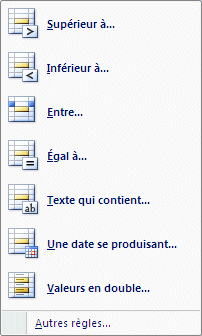 |
Greater than: You can highlight the cells that have values above a limit that you determined. Less than: You can highlight cells that have value below a certain limit. Between: Highlight cells that are between a range of values. Equal To: Highlight cells when its content is equal to a set value. Text that contains: Highlight cells that contain some text. A date occurring: Highlight cells that equals a set date or a range of dates (last week, last month ...) Duplicate values: highlight cells that contain the same values or to unique values. |
![]() Select Manage Rules.
Select Manage Rules.
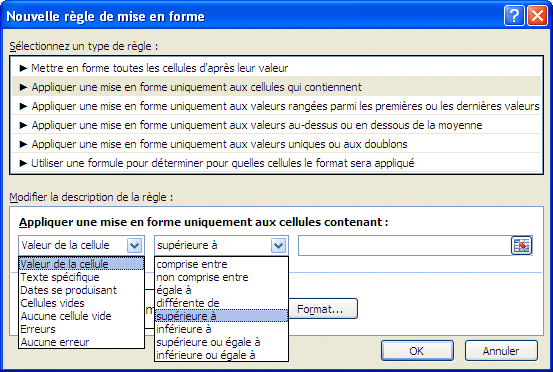 |
You can also manage the conditional formatting rules from this window. It even gives you another option to highlight according to a formula that you created. But, the result of that formula must either be TRUE or FALSE. So, your formula must start with the IF function and contain your formula in the criteria argument of the function. Ex. =IF(A5/B5>=5; TRUE;FALSE). You can create more complex formulas. |
Top/Bottom Rules
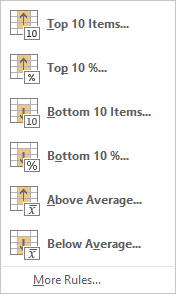 |
Highlight the top or bottom values from a range of cells. You can highlight the top/bottom 10 values, top/bottom 10%, values above or below average. Those are just the options available from this menu. You can have more control on what's highlighted by selecting the More Rules option.
|
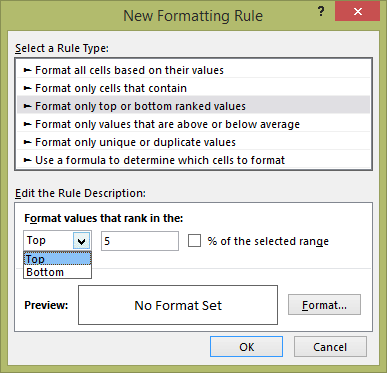 |
This will return you to the Formatting Rule windows with the Format only top or bottom ranked values option selected. You can determine all the options including the cell's formatting for this new rule. |
Data bars
![]() Enter the values from 1 to 5 in the following cells.
Enter the values from 1 to 5 in the following cells.
![]() Select the range of cells from with the values you just entered.
Select the range of cells from with the values you just entered.
![]() On the Home tab, under the Style group of commands, select the Conditional formatting.
On the Home tab, under the Style group of commands, select the Conditional formatting.
![]() Select the Data bar with the color of your choice.
Select the Data bar with the color of your choice.
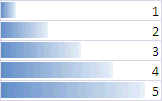 |
Not only can you read the values, but you also have a graphical representation of those values. It's easier to see which has the highest value or the lowest without having to read all the possible values
|
The data bars will adjust to the length of the column. The longer the column, the easier it will be to compare the bars.
You can also add color scales and icon sets to represent your data in a different way.
Color scales
 |
You can select a range of cells and apply color scales to them. The cell's background color will represent its value. In the color scale, the value at the bottom of the scale represents the lowest values. The color on top represents the highest values. You can also select the More Rules option to change how a color scale is applied. |
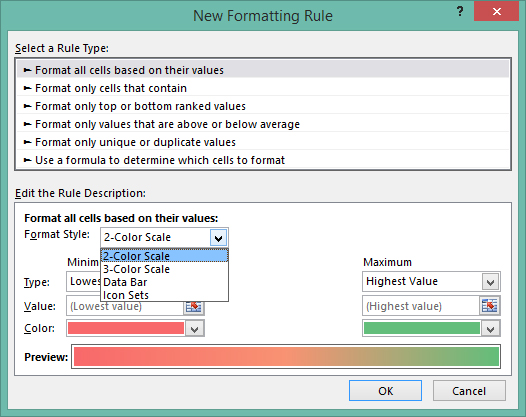 |
From this window, you can apply a 2 or 3 color scale and choose the most appropriate colors for your values. With a 2 color scale, you select a color for the highest and lowest values. Excel will then create a color scale according to the colors you selected. With a 3 color scale, you can select a color for the top, bottom and median values. |
Icon sets
You can also use a set of icons to represent a value. It will appear beside the value inside the cell. As you can see, there is a wide selection of icons to choose from. You can also select Other rules to determine how the icon set will be applied to the values. You can be more selective on how the rules will be applied by selecting the More Rules option. |
You can select the icon set of your choice and at what value should they change to the next icon. You can determine the change by selecting a number, a percentage, a percentile or according to a formula. |
New rule
You can create your own conditionnal formatting rules to determine the type of formatting you want to use and how to apply it. You can also apply many rules to a single cell. |
Clear rules
You can also quickly remove all the rules that were applied to a cell or a range of cells.
Manage rules
You have the opportunity to add, change or remove the rules that you created.
Format as table
 |
|
Cell Styles
 |
You can apply a cell style to a range of cells or to a table. You can quickly change how a worksheet is presented to your audience. |
Cells
 |
Creating a model is only the first part. You also need to adjust it to add or remove data from it. The next options allow you to manage your worksheet and your workbook. You can insert and remove cells, rows and columns by pressing just a few buttons. You can also format it to help its presentation. |
Insert
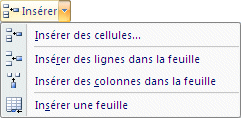 |
You can insert and remove cells, rows and columns by pressing just a few buttons. At any time, you can add a cell, a row, a column in the worksheet. You can even add another worksheet if you need it. |
Delete
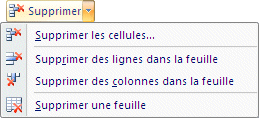 |
This option can remove cells, rows or columns from the worksheet. This may be required to better organize your model. |
Format
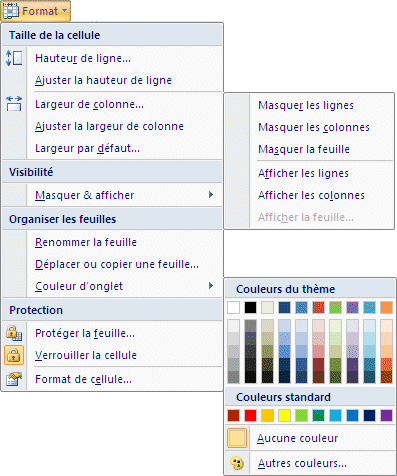 |
Under the format option, you can adjust the length and height of a row or column. You can also mask them temporarily to better view values that are far apart in the worksheet or that you don't want other users to see. You can also change the name on the worksheet's tab or ven its color. You can also protect the entire worksheet so that no user can change the values unless you unprotect some cell that you allow them to change. |
Editing
 |
With these commands, you can work on your worksheet to add formulas, fill in blanks or erase them, sort and filter a data list or search for content in your workbook. |
Autosum and more functions
![]() Follow this link to view the exercise for this command
Follow this link to view the exercise for this command
![]()
![]() Press the triangle pointing down at the end of the Autosum button.
Press the triangle pointing down at the end of the Autosum button.
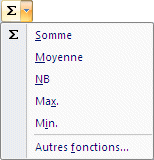 |
Apart from the Sum function, you will have a list of the most recently used functions and access to all the other functions. To access even more functions, select More functions at the bottom of the list. This action will open the Insert Function dialog box. You will be able to search for the function you need from the list of all the functions Excel can provide. |
Fill
Excel offers an Autofill option that you can use to fill cells with predetermined lists or from a range of values. The square on the bottom right of the active cell is the Autofill button. You must the cursor on the autofill button to activate the option. It can also be used to copy text, values or formulas. |
Clear
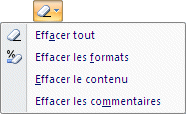 |
At times, you need to remake a section of your worksheet. You can use the options of this section to clear out the content of the cells, it's formatting or comments. |
Sort and Filter
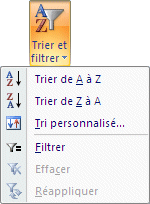 |
Microsoft Excel has always had sort and filter options for data lists. This option is also available under the Data tab. This is where you will find all the instructions to use these options. |
Find and select
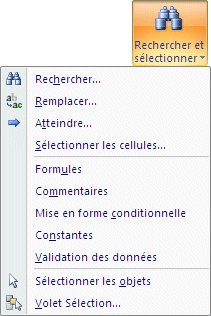 |
At times you need to change part of the data in your model. For example, a product changes name, a company changes address. You can use the options under the Find and Select commands to find and replace data, a cell references in your formulas, or even the content. |
| You like what you read?
Share it with your friends. |